Swollen gums
Gingivitis is a problem that affects a significant proportion of the adult population, yet it is often not taken seriously enough. However, swollen gums can lead to much more serious problems in the long term, so it's worth seeking professional advice as soon as you notice them!

Swollen gums are inflamed
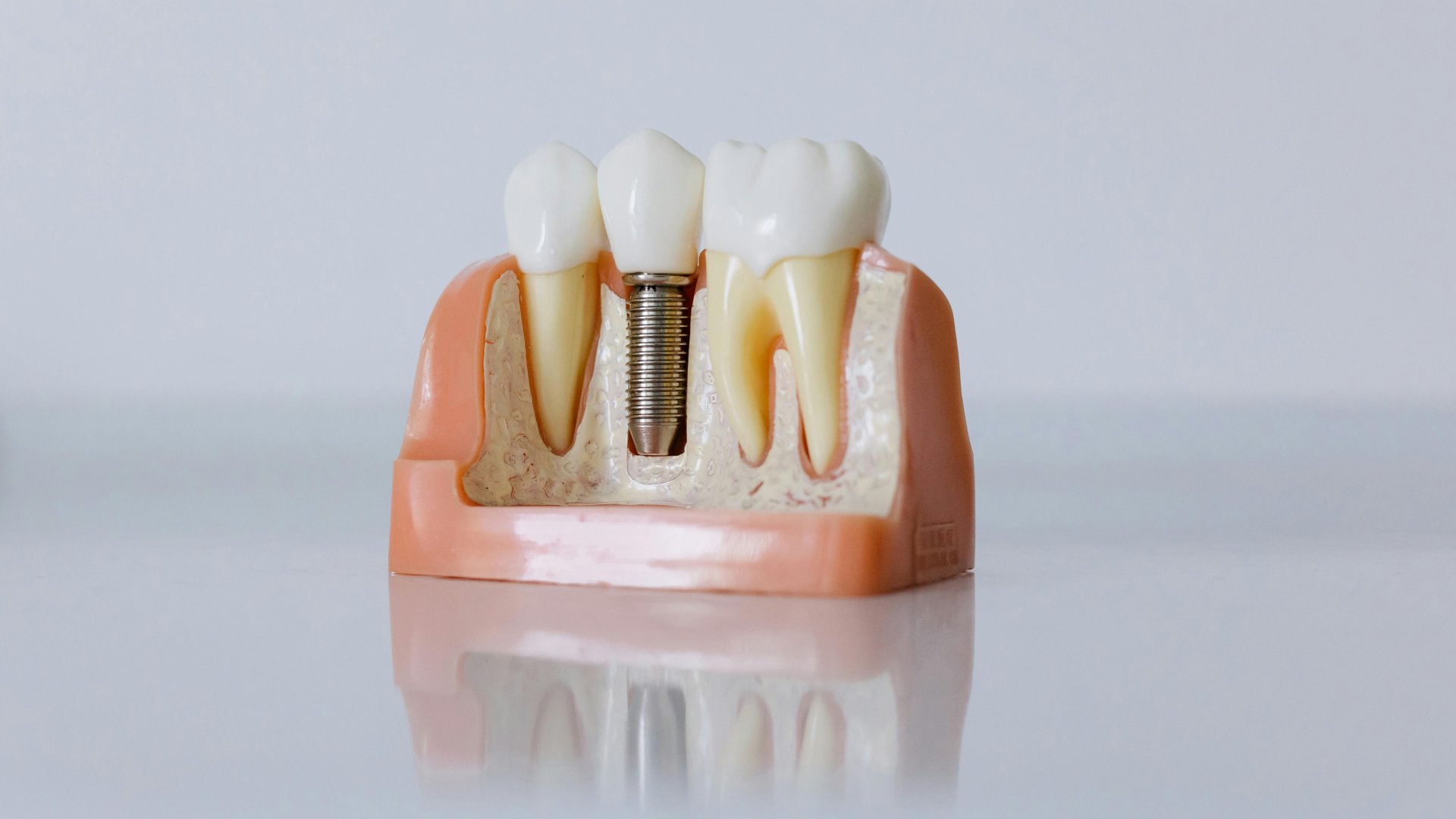
Swollen gums are a warning sign that your gums are inflamed. This is not negligible, because if left untreated, initially swollen gums can lead to tooth loss. The gum, the elastic connective tissue around the tooth roots and the bone tissue surrounding the tooth root are collectively called the periodontium. Inflammation of these tissues around the tooth, the most common of which is gingivitis, is called periodontitis.
What causes swollen gums?
Swollen gums are the first sign of periodontitis, but it's not enough to treat the symptoms, you need to find the cause of the problem. Gingivitis can be caused by a number of things, but the most common are poor oral hygiene, inadequate oral care at home and improper brushing techniques, which can lead to tartar build-up, a real germ. Smoking, alcohol, stress, hormones, certain medications or even poor diet can also be a source of problems.
The development of periodontitis also depends on genetic predisposition, and some people do their best to prevent it, but still find themselves with swollen gums or other telltale symptoms. For example, someone with crowded teeth is more likely to develop gingivitis.
Other telltale symptoms besides swollen gums include
Gingivitis is the earliest form of periodontitis, and in addition to swollen gums, it can also be characterised by darker, red or reddish gums, or even purple gums (healthy gums are pink), bleeding when brushing and often sensitivity in the area.
What happens if swollen gums are not treated?
Swollen gums are often not painful in themselves, which is why many people don't take the problem seriously until it's at a more advanced stage. If left untreated, the initial inflammation of the gums will start to extend deeper into the tooth. At first the gum moves further away from the tooth, the symptoms are the same but more severe, then the inflammation reaches the bone tissue, first the root becomes free and tender, then the bone tissue gradually breaks down. In the long term, swollen gums can even lead to tooth loss.
In the case of swollen gums, it is best to focus on prevention. Are you experiencing symptoms of gingivitis? Don't wait for the problem to get worse, visit our practice!